다양한 설정 형식 지원 - 자바 코드, XML
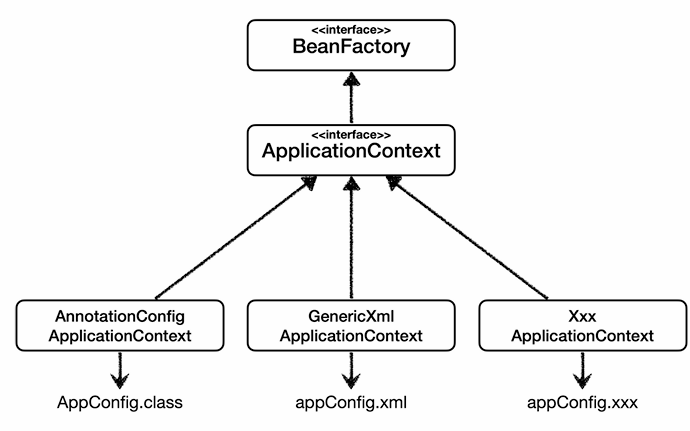
- 스프링 컨테이너는 다양한 형식의 설정 정보를 받아들일 수 있게 유연하게 설계되어있다.
- 자바 코드, XML, Groovy 등등
애노테이션 기반 자바 코드 설정 사용
- new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class)
- AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 클래스를 사용하면서 자바코드로 설정된 정보를 넘기면 된다.
xml 설정 사용
- 최근에는 스프링 부트를 많이 사용하면서 xml 기반의 설정은 잘 사용하지 않는다. 아직 많은 레거시 프로젝트들이 xml 로 되어있고, 또 xml 을 사용하면 컴파일없이 빈 설정 정보를 변경할 수 있다는 장점이 있으므로 한번쯤 배워두는 것도 괜찮다.
- GenericXmlApplicationContext 를 사용하면서 xml 설정 파일을 넘기면 된다.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="memberService" class="hello.core.member.MembrServiceImpl">
<constructor-arg name="memberRepository" ref="memberRepository"/>
</bean>
<bean id="orderService" class="hello.core.Order.OrderServiceImpl">
<constructor-arg name="memberRepository" ref="memberRepository"/>
<constructor-arg name="discountPolicy" ref="discountPolicy"/>
</bean>
<bean id="memberRepository" class="hello.core.member.MemoryMemberRepository" />
<bean id="discountPolicy" class="hello.core.discount.RateDiscountPolicy"/>
</beans>package hello.core;
import hello.core.Order.OrderService;
import hello.core.Order.OrderServiceImpl;
import hello.core.discount.DiscountPolicy;
import hello.core.discount.FixDiscountPolicy;
import hello.core.member.MemberRepository;
import hello.core.member.MemberService;
import hello.core.member.MembrServiceImpl;
import hello.core.member.MemoryMemberRepository;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class AppConfig {
@Bean
public MemberService memberService(){
return new MembrServiceImpl(memberRepository());
}
@Bean
public OrderService orderService(){
return new OrderServiceImpl(
memberRepository(),
discountPolicy());
}
@Bean
public MemberRepository memberRepository(){
return new MemoryMemberRepository();
}
@Bean
public DiscountPolicy discountPolicy(){
return new FixDiscountPolicy();
}
}xml 기반의 appConfig.xml 스프링 설정정보와 자바 코드로 된 AppConfig.java 설정 정보를 비교해보면 거의 비슷하다.
xml 기반으로 설정하는 것은 최근에 거의 사용하지 않는다. (필요시 공식 문서 참조 : Spring Framework )
스프링 빈 설정 메타 정보 - BeanDefinition
스프링은 어떻게 이런 다양한 설정 형식을 지원하는 것일까? 그 중심에는 BeanDefinition 이라는 추상화가 있다.
즉 역할과 구현을 개념적으로 나눈 것이다.
- xml 을 읽어서 BeanDefinition 을 만들면 된다.
- 자바 코드를 읽어서 BeanDefinition 을 만들면 된다.
- 스프링 컨테이너는 자바코드인지, xml 인지 몰라도 된다. 오직 BeanDefinition 만 알면 된다.
- BeanDefinition 을 빈 설정 메타 정보라 한다.
- @Bean, <bean> 당 각각 하나씩 메타정보가 생성된다.
- 스프링컨테이너는 이 메타정보를 기반으로 스프링 빈을 생성한다.

코드레벨로 조금 더 깊이 있게 들어가보자

- AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 는 AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader 를 사용해서 AppConfig.class 를 읽고 BeanDefinition 을 생성한다.
- GenericXmlApplicationContext 는 XmlBeanDefinitionReader 사용해서 appConfig.xml 설정 정보를 읽고BeanDefinition 을 생성한다.
- 새로운 형식의 정보가 추가되면 XXXDefinitionReader 를 만들어서 BeanDefinition 을 생성하면 된다.
BeanDefinition 정보
BeanClassName : 생성할 빈의 클래스 명 (자바 설명처럼 팩토리 역할의 빈(AppConfig.class)을 사용하면 없음)
factoryBeanName : 팩토리 역할의 빈을 사용할 경우, ex) appConfig
factoryMethodName : 빈을 생성할 팩토리 메서드 지정 , ex) memberService
Scope : 싱글톤(기본값)
lazyInit: 스프링 컨테이너를 생성할 때 빈을 생성하는 것이 아니라, 실제 빈을 사용할 때 까지 최대한 생성을 지연 처리 하는지 여부
InitMethodName : 빈을 생성하고, 의존관계를 적용한 뒤에 호출되는 초기화 메서드 명
DestroyMethodName : 빈의 생명주기가 끝나서 제거하기 직전에 호출되는 메서드 명
Constructor arguments, Properties : 의존관계 주입에서 사용한다. (자바 설정 처럼 팩토리 역할의 빈을 사용 하면 없음
ex ) beanDefinitionName = memberService beanDefinition = Root bean: class [null]; scope=; abstract=false; lazyInit=null; autowireMode=3; dependencyCheck=0; autowireCandidate=true; primary=false; factoryBeanName=appConfig; factoryMethodName=memberService; initMethodNames=null; destroyMethodNames=[(inferred)]; defined in hello.core.AppConfig

- BeanDefinition을 직접 생성해서 스프링 컨테이너에 등록할 수 도 있다. 하지만 실무에서 BeanDefinition을 직접 정의하거나 사용할 일은 거의 없다. 어려우면 그냥 넘어가면 된다!
- BeanDefinition에 대해서는 너무 깊이있게 이해하기 보다는, 스프링이 다양한 형태의 설정 정보를 BeanDefinition으로 추상화해서 사용하는 것 정도만 이해하면 된다.
- 가끔 스프링 코드나 스프링 관련 오픈 소스의 코드를 볼 때, BeanDefinition 이라는 것이 보일 때가 있다. 이때 이러한 메커니즘을 떠올리면 된다
package hello.core.beanfind;
import hello.core.AppConfig;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.DisplayName;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.GenericXmlApplicationContext;
public class BeanDefinitionTest {
// AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
GenericXmlApplicationContext ac = new GenericXmlApplicationContext("appConfig.xml");
@Test
@DisplayName("빈 설정 메타정보 확인")
void findApplicationBan() {
String[] beanDefinitionNames = ac.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for(String beanDefinitionName : beanDefinitionNames){
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = ac.getBeanDefinition(beanDefinitionName);
if(beanDefinition.getRole() == BeanDefinition.ROLE_APPLICATION){
System.out.println("beanDefinitionName = " + beanDefinitionName + " beanDefinition = " + beanDefinition);
}
}
}
}'Spring' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [스프링 핵심 원리 - 기본편] 싱글톤 패턴 2 (2) | 2024.10.17 |
|---|---|
| [스프링 핵심 원리 - 기본편] 싱글톤 패턴 1 (0) | 2024.10.17 |
| [스프링 핵심 원리 - 기본편] 스프링 컨테이너와 스프링 빈 2 (0) | 2024.10.16 |
| [스프링 핵심 원리 - 기본편] 스프링 컨테이너와 스프링 빈 1 (0) | 2024.10.15 |
| [스프링 핵심 원리 - 기본편] 스프링 핵심 원리 이해3 - 객체 지향 원리 적용 (3) | 2024.10.14 |