인터럽트 - 시작 1
특정 스레드의 작업을 중간에 중단하려면 어떻게 해야 할까?
package thread.control.interrupt;
import static util.MyLogger.log;
import static util.ThreadUtils.sleep;
public class ThreadStopMainV1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyTask task = new MyTask();
Thread thread = new Thread(task, "work");
thread.start();
sleep(4000);
log("작업 중단 지시 runFlag = true");
task.runFlag = false;
}
static class MyTask implements Runnable {
volatile boolean runFlag = true;
@Override
public void run() {
while(runFlag) {
log("작업 중");
sleep(3000);
}
log("자원 정리");
log("자원 종료");
}
}
}- 특정 스레드의 작업을 중단하는 가장 쉬운 방법은 변수를 사용하는 것이다.
- 여기서는 runFlag를 사용해서 work 스레드에 작업 중단을 지시할 수 있다.
- 작업 하나에 3초가 걸린다고 가정하고, sleep(3000)을 사용하자.
- main 스레드는 4초 뒤에 작업 중단을 지시한다.
14:58:27.520 [ work] 작업 중
14:58:30.525 [ work] 작업 중
14:58:31.510 [ main] 작업 중단 지시 runFlag=false
14:58:33.532 [ work] 자원 정리
14:58:33.533 [ work] 작업 종료- work 스레드는 runFlag 가 true 인 동안 계속 실행된다.

프로그램 시작 4초 뒤에 main 스레드는 runFlag를 false로 변경한다.
work 스레드는 while(runFlag)에서 runFlag의 조건이 false로 변한 것을 확인하고 while 문을 빠져나가면서 작업을 종료한다.
문제점
실행을 해보면 알겠지만 main 스레드가 runFlag == false를 통해 작업 중단을 지시해도, work 스레드가 즉각 반응하지 않는다. 로그를 보면 작업 중단 지시 2초 정도 이후에 자원을 정리하고 작업을 종료한다.( while 문을 3초에 한 번씩 확인함 )
14:58:27.520 [ work] 작업 중
14:58:30.525 [ work] 작업 중
14:58:31.510 [ main] 작업 중단 지시 runFlag=false
14:58:33.532 [ work] 자원 정리 //2초 정도 경과후 실행
14:58:33.533 [ work] 작업 종료
이 방식의 가장 큰 문제는 다음 코드 sleep()에 있다.
while (runFlag) {
log("작업 중");
sleep(3000);
}
- main 스레드가 runFlag를 false 로 변경해도, work 스레드는 sleep(3000) 을 통해 3초간 잠들어 있다. 3초간의 잠이 꺤 다음에 while(runFlag) 코드를 실행해야, runFlag 를 확인하고 작업을 중단할 수 있다.
- 참고로 runFlag를 변경한 2초라는 시간이 지난 히우에 작업이 종료되는 이유는 work 스레드가 3초에 한번씩 깨어나서 runFlag 를 확인하는데, main 스레드가 4초에 runFlag 를 변경했기 때문이다.
- work 스레드 입장에서 보면 두 번째 sleep()에 들어가고 1초 후 main 스레드가 runFlag를 변경한다. 3초간 sleep() 이므로 아직 2초가 더 있어야 깨어난다.
- 어떻게 하면 sleep()처럼 스레드가 대기하는 상태에서 깨우고, 작업도 빨리 종료할 수 있을까?
인터럽트 - 시작 2
예를 들어서, 특정 스레드가 Thread.sleep()을 통해 쉬고 있는데, 처리해야 하는 작업이 들어와서 해당 스레드를 급하게 꺠워야 할 수 있다. 또는 sleep()으로 쉬고 있는 스레드에게 더는 일이 없으니, 작업 종료를 지시할 수 도 있다.
인터럽트를 사용하면 , WAITING, TIMED_WAITTING 같은 대기 상태의 스레드를 직접 깨워서, 작동하는 RUNNABEL 상태로 만들 수 있다.
package thread.control.interrupt;
import static util.MyLogger.log;
import static util.ThreadUtils.sleep;
public class ThreadStopMainV2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyTask task = new MyTask();
Thread thread = new Thread(task, "work");
thread.start();
sleep(4000);
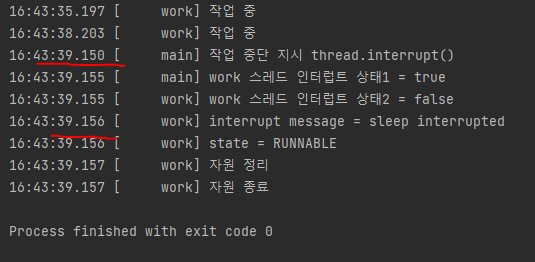
log("작업 중단 지시 thread.interrupt()");
thread.interrupt();
log("work 스레드 인터럽트 상태1 = " + thread.isInterrupted());
}
static class MyTask implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
while(true) {
log("작업 중");
Thread.sleep(3000);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log("work 스레드 인터럽트 상태2 = " + Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted());
log("interrupt message = " + e.getMessage());
log("state = " + Thread.currentThread().getState());
}
log("자원 정리");
log("자원 종료");
}
}
}

- 예제의 run()에서는 인터럽트를 이해하기 위해, 직접 만든 sleep() 대신에 Thread.sleep()를 사용하고 , try ~ catch 도 사용하자.
- 특정 스레드의 인스턴스에 interrupt() 메서드를 호출하면, 해당 스레드는 인터럽트가 발생한다.
- 인터럽트가 발생하면 해당 스레드에 IntegerrptedException 이 발생한다.
- 이때 인터럽트를 받은 스레드는 대기 상태에서 깨어나 RUNNABLE 상태가 되고, 코드를 정상 수행한다
- 이때 InterruptedExcepton을 catch로 잡아서 정상 흐름으로 변경하면 된다.
- 참고로 interrupt()를 호출했다고 즉각 InterruptedException 이 발생하는 것이 아니다. 오직 sleep()처럼 InterruptedException을 던지는 메서드를 호출하거나 또는 호출 중일 때 예외가 발생한다.
- 예를 들어서 위 코드에서 while(true) , log("작업 중")에서 InterruptedException 이 발생하지 않는다.
- Thread.sleep()처럼 InterruptedException을 던지는 메서드를 호출하거나 또는 호출하며 대기 중일 때 예외가 발생한다.
인터럽트 - 시작 3
그런데 앞선 코드에서 한 가지 아쉬운 부분이 있다
while (true) { //인터럽트 체크 안함
log("작업 중");
Thread.sleep(3000); //여기서만 인터럽트 발생
}다음과 같이 인터럽트의 상태를 확인하면, 더 빨리 반응할 수 있을 것이다.
while (인터럽트_상태_확인) { //여기서도 인터럽트 상태 체크
log("작업 중");
Thread.sleep(3000); //인터럽트 발생
}이 코드와 같이 인터럽트의 상태를 확인하면 while문을 체크하는 부분에서 더 빠르게 while문을 빠져나갈 수 있다. 물론 이 예제의 경우 코드가 단순해서 실질적인 차이는 매우 작다.
추가로 인터럽트의 상태를 직접 확인하면, 다음과 같이 인터럽트를 발생시키는 sleep()과 같은 코드가 없어도 인터럽트 상태를 직접 확인하기 때문에 while문을 빠져나갈 수 있다
while (인터럽트_상태_확인) { //여기서도 체크
log("작업 중");
}package thread.control.interrupt;
import static util.MyLogger.log;
import static util.ThreadUtils.sleep;
public class ThreadStopMainV3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyTask task = new MyTask();
Thread thread = new Thread(task, "work");
thread.start();
sleep(100); // 시간을 줄임
log("작업 중단 지시 thread.interrupt()");
thread.interrupt();
log("work 스레드 인터럽트 상태1 = " + thread.isInterrupted());
}
static class MyTask implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
while(!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) {
log("작업 중");
}
log("work 스레드 인터럽트 상태2 = " + Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted());
try {
log("자원 정리");
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log("자원 정리 실패 - 자원 정리 중 인터럽트 발생");
log("work 스레드 인터럽트 상태3 = " +
Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted());
}
log("작업 종료");
}
}
}
여기까지 보면 아무런 문제가 없어 보인다. 하지만 이 코드에는 심각한 문제가 있다.
바로 ` work` 스레드의 인터럽트 상태가 ` true` 로 계속 유지된다는 점이다.
앞서 인터럽트 예외가 터진 경우 스레드의 인터럽트 상태는 ` false` 가 된다.
반면에 ` isInterrupted()` 메서드는 인터럽트의 상태를 변경하지 않는다.
단순히 인터럽트의 상태를 확인만 한다.
` work` 스레드는 이후에 자원을 정리하는 코드를 실행하는데, 이때도 인터럽트의 상태는 계속 ` true` 로 유지된다.
이때 만약 인터럽트가 발생하는 ` sleep()` 과 같은 코드를 수행한다면, 해당 코드에서 인터럽트 예외가 발생하게 된다
. 이것은 우리가 기대한 결과가 아니다! 우리가 기대하는 것은 ` while()` 문을 탈출하기 위해 딱 한 번만 인터럽트를 사용하는 것이지, 다른 곳에서도 계속해서 인터럽트가 발생하는 것이 아니다.
- 자바에서 인터럽트 예외가 한 번 발생하면, 스레드의 인터럽트 상태를 다시 정상( ` false` )으로 돌리는 것은 이런 이유 때문이다.
- 스레드의 인터럽트 상태를 정상으로 돌리지 않으면 이후에도 계속 인터럽트가 발생하게 된다.
- 인터럽트의 목적을 달성하면 인터럽트 상태를 다시 정상으로 돌려두어야 한다.

인터럽트 - 시작 4
Thread.interrupted()
스레드의 인터럽트 상태를 단순히 확인만 하는 용도라면 isInterrupted() isInterrupted()를 사용하면 된다
하지만 직접 체크해서 사용할 때는` Thread.interrupted()를 사용해야 한다.
이 메서드는 다음과 같이 작동한다
- 스레드가 인터럽트 상태라면 true를 반환하고, 해당 스레드의 인터럽트 상태를 false로 변경한다.
- 스레드가 인터럽트 상태가 아니라면 false를 반환하고, 해당 스레드의 인터럽트 상태를 변경하지 않는다.
package thread.control.interrupt;
import static util.MyLogger.log;
import static util.ThreadUtils.sleep;
public class ThreadStopMainV4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyTask task = new MyTask();
Thread thread = new Thread(task, "work");
thread.start();
sleep(100); // 시간을 줄임
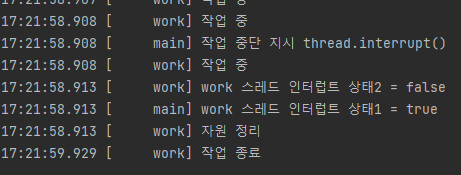
log("작업 중단 지시 thread.interrupt()");
thread.interrupt();
log("work 스레드 인터럽트 상태1 = " + thread.isInterrupted());
}
static class MyTask implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
while(!Thread.interrupted()) { // 인터럽트 상태 변경 O
log("작업 중");
}
log("work 스레드 인터럽트 상태2 = " + Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted());
try {
log("자원 정리");
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log("자원 정리 실패 - 자원 정리 중 인터럽트 발생");
log("work 스레드 인터럽트 상태3 = " +
Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted());
}
log("작업 종료");
}
}
}
자바는 인터럽트 예외가 한 번 발생하면, 스레드의 인터럽트 상태를 다시 정상( ` false ` )으로 돌린다.
스레드의 인터럽트 상태를 정상으로 돌리지 않으면 이후에도 계속 인터럽트가 발생하게 된다.
인터럽트의 목적을 달성하면 인터럽트 상태를 다시 정상으로 돌려두어야 한다.
프린터 예제 1 - 시작
package thread.control.interrupt;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentLinkedQueue;
import static util.MyLogger.log;
import static util.ThreadUtils.sleep;
public class MyPrinterV1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Printer printer = new Printer();
Thread printerThread = new Thread(printer, "printer");
printerThread.start();
Scanner userInput = new Scanner(System.in);
while (true) {
log("프린터할 문서를 입력하세요. 종료 (q): ");
String input = userInput.nextLine();
if(input.equals("q")){
printer.work = false;
break;
}
printer.addJob(input);
}
}
static class Printer implements Runnable {
volatile boolean work = true;
Queue<String> jobQueue = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<>();
@Override
public void run() {
while (work) {
if (jobQueue.isEmpty()){
continue;
}
String job = jobQueue.poll();
log("출력 시작 " + job + " , 대기 문서 " + jobQueue);
sleep(3000); // 출력에 걸리는 시간
log("출력 완료 " + job);
}
log("프린터 종료");
}
public void addJob(String input) {
jobQueue.offer(input);
}
}
}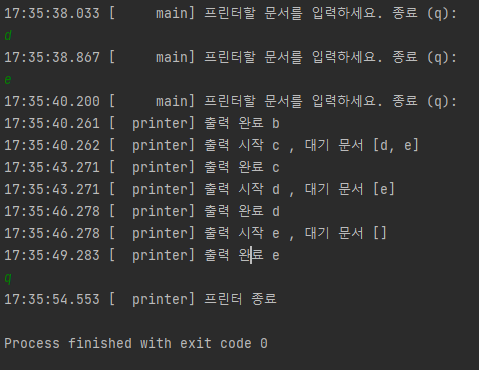

- main 스레드 : 사용자의 입력을 받아서 Printer 인스턴스의 jobQueue에 담는다.
- printer 스레드 : jobQueue 가 있는지 확인한다.
- jobQueue에 내용이 있으면 poll()을 이용해서 꺼낸 다음에 출력한다.
- 출력하는 데 약 3초 시간이 걸린다. 여기서 sleep(3000)를 사용해서 출력 시간을 가상으로 구현했다.
- 출력을 완료하며 while 문을 다시 반복한다.
- 만약 jobQueue 가 비었다면 continue를 사용해서 다시 while 문을 반복한다.
- 이렇게 jobQueue에 출력한 내용이 들어올 때까지 계속 확인한다.

yield - 양보하기
어떤 스레드를 얼마나 실행할지는 운영체제가 스케줄링을 통해 결정한다. 그런데 특정 스레드가 크게 바쁘지 않은 상황이어서 다른 스레드에 CPU 실행 기회를 양보하고 싶을 수 있다. 이렇게 양보하면 스케줄링 큐에 대기 중인 다른 스레드가 CPU 실행 기회를 더 빨리 얻을 수 있다.
package thread.control.yield;
import static util.MyLogger.log;
import static util.ThreadUtils.sleep;
public class YieldMain {
static final int THREAD_COUNT = 1000;
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < THREAD_COUNT; i++) {
Thread thread = new Thread(new MyRunnable());
thread.start();
}
}
static class MyRunnable implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " - " + i);
// 1. empty
// sleep(1); // 2. sleep
// Thread.yield(); // 3. yield
}
}
}
}
- sleep(1)을 사용해서 스레드의 상태를 1밀리 초 동안 아주 잠깐 RUNNABLE ->TIME_WAITING으로 변경한다.
- 이렇게 되면 스레드는 CPU 자원을 사용하지 않고, 실행 스케줄링에서 잠시 제외된다. 1밀리 초의 대기시간 이후 다시 TIME_WAITING -> RUNNABLE 상태가 되면서 실행 스케줄링에 포함된다.
- 결좌적으로 TIME_WAITING 상태가 되면서 다른 스레드에 실행을 양보하게 된다. 그리고 스케줄링 큐에 대기 중인 다른 스레드가 CPU의 실행 기회를 빨리 얻을 수 있다.
하지만 이 방식은 RUNNABLE -> TIMED_WAITING -> RUNNABLE로 변경되는 복잡한 과정을 거치고, 또 특정 시간만큼 스레드가 실행되지 않는 단점이 있다.
예를 들어서 양보할 스레드가 없다면 차라리 나의 스레드를 더 실행하는 것이 나은 선택일 수 있다. 이 방법은 나머지 스레드가 대기 상태로 쉬고 있어도 내 스레드까지 잠깐 실행되지 않는다. 쉽게 이야기해서 양보할 사람이 없는데 혼자서 양보한 이상한 상황이 될 수 있다.

자바의 스레드가 RUNNABLE 상태일 때, 운영체제의 스케줄링은 다음과 같은 상태를 가질 수 있다.
- 실행 상태 (Running) : 스레드가 CPU 에서 실제로 실행 중이다.
- 실행 대기 상태(Ready) : 스레드가 실행 될 준비가 되었지만, CPU 가 바빠서 스케줄링 큐에서 대기 중이다.
운영체제는 실행 상태의 스레드들을 잠깐만 실행하고 실행 대기 상태로 만든다. 그리고 실행 대기 상태의 스레드들을 자깐만 실행 상태로 변경해서 실행한다. 이 과정을 반복한다. 참고로 자바에서는 두 상태를 구분할 수 는 없다.
자바에서 Thread.yield() 메서드를 호출하면 현재 실행 중인 스레드가 CPU 를 양보하도록 힌트를 준다. 이는 스레드가 자신에게 할당된 실행 시간을 포기하고 다른 스레드에게 실행 기회를 주도록 한다. 참고로 yield() 는 운영체제의 스케줄러에게 단지 힌트를 제공할 뿐, 강제적인 실행 순서를 지정하지 않는다. 그리고 반드시 다른 스레드가 실행되는 것도 아니다.
yield() 는 RUNNABLE 상태를 유지하기 떄문에, 쉽게 이야기해서 양보할 사람이 없다면 본인 스레드가 실행될 수 있다.
참고로 최근에는 10코어 이상의 CPU도 많기 때문에 스레드 10개 정도만 만들어서 실행하면, 양보가 크게 의미가 없 다. 양보해도 CPU 코어가 남기 때문에 양보하지 않고 계속 수행될 수 있다. CPU 코어 수 이상의 스레드를 만들어야 양 보하는 상황을 확인할 수 있다. 그래서 이번 예제에서 1000개의 스레드를 실행한 것이다
인터럽트 적용! & - yield 도입
package thread.control.interrupt;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentLinkedQueue;
import static util.MyLogger.log;
public class MyPrinterV3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Printer printer = new Printer();
Thread printerThread = new Thread(printer, "printer");
printerThread.start();
Scanner userInput = new Scanner(System.in);
while (true) {
log("프린터할 문서를 입력하세요. 종료 (q): ");
String input = userInput.nextLine();
if(input.equals("q")){
printerThread.interrupt();
break;
}
printer.addJob(input);
}
}
static class Printer implements Runnable {
volatile boolean work = true;
Queue<String> jobQueue = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<>();
@Override
public void run() {
while (!Thread.interrupted()) {
if (jobQueue.isEmpty()){
Thread.yield(); // 추가
continue;
}
String job = jobQueue.poll();
log("출력 시작 " + job + " , 대기 문서 " + jobQueue);
try {
Thread.sleep(3000); // 출력에 걸리는 시간
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log("인터럽트!");
break;
}
log("출력 완료 " + job);
}
log("프린터 종료");
}
public void addJob(String input) {
jobQueue.offer(input);
}
}
}
'JAVA' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [JAVA] String intern() (1) | 2024.11.15 |
|---|---|
| [JAVA] 동기화 - synchronized (2) | 2024.11.13 |
| [JAVA] 스레드 Join (0) | 2024.11.12 |
| [JAVA] Runnable 을 만드는 다양한 방법 (0) | 2024.11.11 |
| [JAVA] 데몬 스레드 (1) | 2024.11.11 |